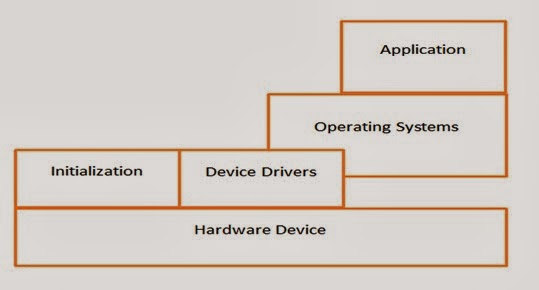
Embedded System Architecture
Embedded System:-
Embedded System is the combination of
Hardware and Software. Embedded System consists of hardware components like,
· Processor
· Peripherals
· Controllers
· Buses
Processor:-
· Processor is the heart
of the Embedded Systems
· Processor controls the
Embedded Device
· Ex:- 8085,
8086
Peripherals:-
· Any Embedded System
that interact with the outside world need some form of peripheral devices.
· A peripheral device
performs input and output functions for the chip.
· Ex:- Timer,
ADC, UART, SPI, I2C, CAN and WDT
Controllers:-
There are 2 types of controllers
1. Memory
Controllers
2. Interrupt
Controllers
Memory Controllers:-
· Memory Controllers
connect different types of memory to the bus.
· On Reset, Memory
controllers are initialized.
· Ex:- In ARM Platform, the different types of memory
like Flash, RAM, EEPROM, DRAM are connected to memory controllers.
Memory:-
An Embedded System
consists some form of memory to store and execute programs.
Cache:-
It is the memory
device, which places in between CPU Core and Main Memory.
Interrupt
Controllers:-
An
Interrupt Controller provides programmable software to determine which
peripheral or device can interrupt the processor.
Buses:-
Buses
are used to communicate between the different parts of the device.
In
ARM Processor, AMBA
is on-chip internal bus is used to connect the processor and peripherals
together.
There
are 2 types of Buses,
1. AHB
Bus
2. VPB
Bus
· A Bus has two
architecture levels. The First is a physical level that covers the electrical characteristics
and the bus width (16, 32 and 64 bits).
· The Second level deals
with the Protocol.
Embedded System Software Components:-
Initialization Code:-
· Initialization Code is
the first code executed on the board.
· It sets up the minimal
parts of the board and give the control to an operating system.
· There are different
tasks are done in 3 Phases :
1. Initial
Hardware Design
2. Diagnostics
3. Booting
Initial Hardware Design:-
· It initializes the CPU
Clock
· It initializes the Memory
· It initializes the
stack pointers for all the modes
· It gives the basic
branch instructions for all the interrupts and exceptions
· It remaps the memory
Diagnostics:-
The primary purpose of Diagnostic code
is fault identification and isolation.
Booting:-
Booting involves loading an operating
system and give the control to an Operating System.
Firmware:-
A System may require firmware support to
boot an operating system.
Firmware is an important part of an
embedded system in which the first code is ported and executed on a new
platform.
There are 2 popular industry standard
firmware packages for ARM based systems.
1. ARM
Firmware Suit
2. Red
Hat’s Red Boot
The firmware is deeply embedded low
level software that provides an interface between the hardware and the operating
system.
It resides in the ROM and executes when
power is applied to the embedded hardware system.
Device Drivers:-
The Device Drivers provide a consistent
software interface to the peripherals on the hardware device.
The HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer)
software communicates with the specific hardware peripherals called a Device
Driver.
A Device Driver provides a standard
application programming interface (API) to read and write to a specific
peripherals like USB, UART, CAN, SPI etc.
We can send the commands through a
Command Line Interpreter (CLI) to target platform.
For Embedded Systems, the CLI is
commonly controlled through a Host terminal application.
Operating System:-
The Operating System provides an
Infrastructure to control applications and manage hardware resources.
Operating System organizes the System
Resources :
· Peripherals
· Memory
Operating System classified into two
types :
1. RTOS
(Real Time Operating System)
2. GPOS
(General Purpose Operating System)
RTOS:-
· RTOS provides
guaranteed response times to an events.
· Systems running on RTOS
generally don’t have Secondary Storage.
GPOS:-
· It requires memory
management unit and it has secondary storage
· Ex:-
Linux, Windows
Embedded Operating System:-
· The initialization sets
up the variables, data structures and hardware devices by the operating system.
· All interrupts and
exceptions require a handler. For unused interrupts and exceptions a dummy
handler must be installed.
· A periodic timer is
required for pre-emptive operating system.
· A scheduler is an
algorithm that schedules the tasks to execute.
· A context switch saves
the state of the current task and loads the state of the next task.
Article by:-

Venkatesh Enjam
Project Engineer - 1
CDAC R & D
Bangalore
posted data:- 05/02/2014
Article by:-

Venkatesh Enjam
Project Engineer - 1
CDAC R & D
Bangalore
posted data:- 05/02/2014



0 comments:
Post a Comment